A relatively thorough and comprehensive job was done (with seven long videos!) covering the melismatic morae vocis in the Vatican Edition, but what about morae for syllabic chants? The only principle we have to apply is that the ritardando should be very pronounced for a double bar, less so for a single bar, even less pronounced for a half bar, and slight for a quarter bar. Furthermore, even this principle does not hold true when the double bar is used merely to signify a change of singers, as in the Gloria and Credo).
First, the good news. Every school agrees on the placement of the mora vocis for words accented on the antepenultimate syllable, like Dóminus, Génitum, Lúmine, and Hómines. Dom Gajard calls these “dactyls” (Page 60, The Rhythm of Plainsong). The mora vocis is always placed on the very last syllable:
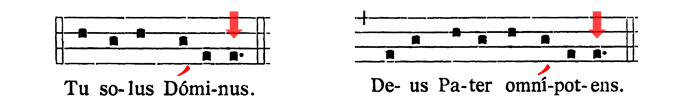
Now, the bad news. There is no agreement among the various schools when it comes to words with a tonic accent on the penult, like Déus, Chríste, Pátris, and Múndi. Dom Gajard calls these “spondees” (Page 60, The Rhythm of Plainsong).
In general, the German editions tend to lengthen both ending syllables, as in the following excerpt from Dom Johner (Page 29, A New School of Gregorian Chant):

Others find that a little too heavy, so they mark these as in the 1917 edition by Schwann (Page 175, Römisches Gradualbuch):

By reading Pages 39-40 (PDF), the reader will see that Joseph Gogniat tries to “play both sides of the fence.” However, here Gogniat is at odds with his teacher, the great Dr. Peter Wagner. If the reader examines Peter Wagner’s Kyriale (PDF), he will notice that Wager doubles each and every spondee, without fail:

For the record, Gogniat claims in his Author’s Preface (Page 6, Little Grammar of Gregorian Chant) that Wagner was not proud of his numerous transcriptions.
No doubt the reader is curious as to how Dom Mocquereau handled these syllabic spondees. In general, the traditional Solesmes editions alternate back and forth between a double “dot” and a single “dot.” Sometimes, they appear to be added “without rhyme or reason,” for instance when they use a double dot before a quarter breath, yet a single dot before a half bar:

Perhaps we could say (speaking in general) that Solesmes prefers the double dot before a double bar, whereas normally a single dot suffices. However, there are certainly plenty of “exceptions” to this rule:

Occasionally, Solesmes goes “above and beyond the call of duty,” adding morae where none are indicated (I am referring to the blue asterisk):

Mocquereau’s dual method for treating Latin spondees cuased Dom Gregory Murray to go into hysterics in his pamphlet entitled Accentual Cadences in Gregorian Chant (PDF). Perhaps Dom Murray would have been consoled to hear the Solesmes monks sing, as they frequently did not follow the markings in their books. To give just one example, listen to the above example as sung by Solesmes, and see if they do not, in fact, lengthen both notes for the spondee “Patri”:

However, Mocquereau’s treatment of spondees seems to have “evolved.” Perhaps he felt that his 1903 markings were too “heavy.” In any event, compare the above markings (1903) to those added a decade later, when Mocquereau added markings to the 1912 Antiphonale (Vatican Edition):

Incidentally, his 1903 Liber Usualis was Mocquereau’s crowning achievement in life, and he was utterly crushed when the Vatican chose Pothier’s 1883 edition over his in 1905.
Without going too far off subject, I would like to mention that studying the evolution of Mocquereau’s various theories and rhythmic markings is quite fascinating, especially the evolution of the ictus. At one point, Mocquereau was marking the ictus with little “dots,” but this was later abandoned:

According to Solesmes, it was abandoned because singers were interpreting the “dot notes” staccato! Speaking of the evolution of Solesmes’ editions, glance through the final sections of the Reims & Cambrai (PDF), and you will see many rare items.
Having read all this, and studied the examples, the reader is now in a position to explain the difference between a Bistropha (two punctums in a row on one syllable) and a dotted note:

The Bistropha is in the pure Vaticana and cannot be changed. It comes from the Gregorian MSS (although we don’t know which precise MSS Pothier favored). The dotted note is a suggestion by Mocquereau that the singer might want to lengthen the note. The dotted note is a direct response to the bars found in the Vaticana. Furthermore, the bar—whether double, full, half, or quarter—is one of the very few rhythmic indications in the Vaticana.
Perhaps the reader is curious to know, “Why do we slow down at the various bars?” The answer is quite simple: it is unimaginable to us that mediæval singers would not have slowed down toward the end of phrases. Granted, we have no proof of this, but it seems to be generally assumed. Try singing straight through to the end of a phrase without any type of ritardando: the effect is not a pleasant one.
We have a window into Pothier’s opinions in this area through his recordings. Here is a video example recorded in 1904, with Pothier directing the Choir of the Benedictines of San Anselmo:
What I found most interesting on my trip, without exception, was the city of Laon, its cathedral and library. It contains a great number of manuscripts (about 500) including practically all of Prémontré. The Antiphonal I wished to see is from the eleventh century, judging from the neumes that resemble those of the Albi and Aries Antiphonaries in the Imperial Library. It is a different system of notation from that of St. Gall. In spite of that, in the Laon manuscripts are found the romanian letters explained by Notker. These letters at Laon, even more so than at St. Gall, confirm, as I have assured myself, Guido d’ Arezzo’s theory about the long final of the musical symbols, mora ultima vocis. I shall go to Colmar on Monday to obtain, if I can, those of Murbach.
[Dom Joseph Pothier, Letter from Soultzmatt, 1865]For the sake of completeness, here is a recording from 1904, with Dom André Mocquereau conducting Pupils of French Seminary in Rome:
GO BACK
